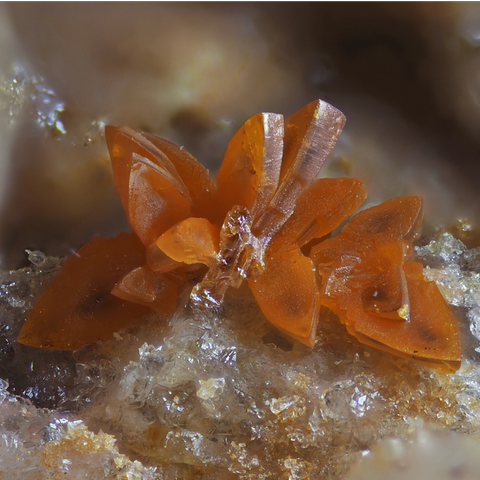
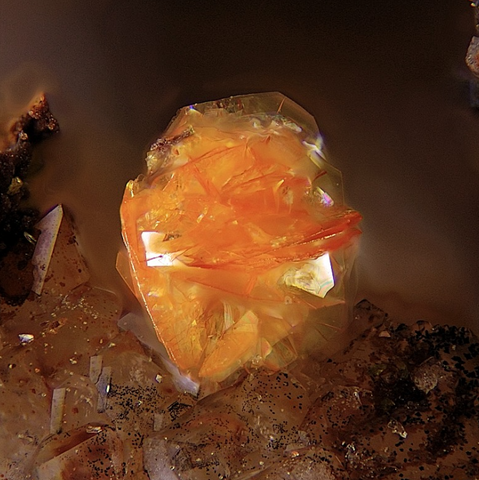
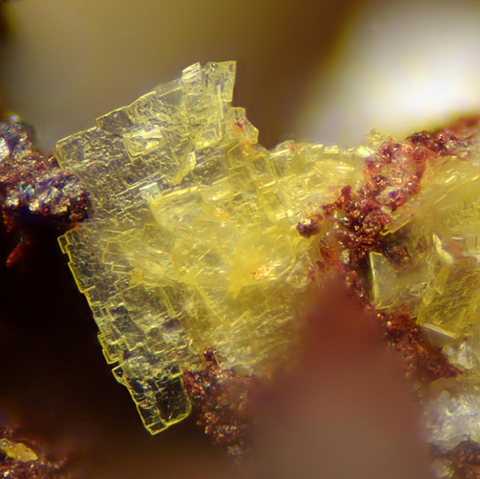
BISMUTITE
Class : Carbonates, Nitrates, Borates
Subclass : Anhydrous carbonates
Crystal System : Tetragonal
Chemistry : Bi2O2(CO3)
Rarity : Fairly common
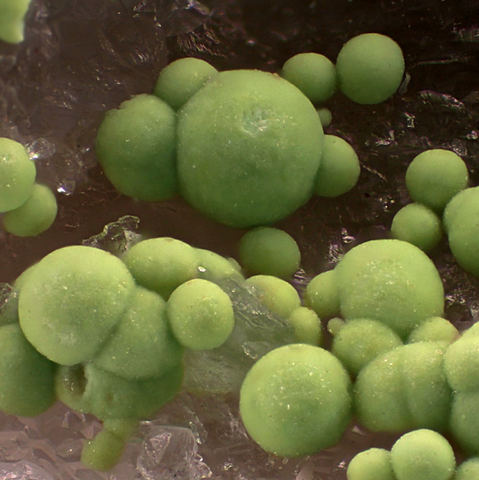
Bismutite is the usual supergene alteration mineral of native bismuth and bismuthinite. It is found in the oxidation zone of hydrothermal deposits containing bismuth, in particular epithermal gold deposits and polymetallic veins of the "Ni-Co-Bi-Ag-U" type, sometimes in pegmatites. Its name refers to its chemical composition : bismuth. Crystals are very rare, bismutite essentially constitutes powdery masses or spheroidal aggregates with an earthy break, medium to dark gray or olive brown, rarely white to pale yellow. Its identification is possible thanks to its cold effervescence in acids and its high density (8.1 to 8.3).
Main photo : Bismutite from Clara Mine, Baden-Württemberg, Germany © Michael Förch
Bismutite in the World
Twinning and special crystallizations
No twin known for this mineral species.
Fakes and treatments
No fake identify for this mineral species.
Hardness : 2.5 to 3.5
Density : 6.7 to 7.4
Fracture : Irregular
Trace : Gray
TP : Translucent to transparent
RI : 2.120 to 2.300
Birefringence : 0.130 to 0.160
Optical character : Uniaxial
Pleochroism : Visible
Fluorescence : None
Solubility : Acids
Magnetism : None
Radioactivity : None