What are lanthanides in geology ?
Lanthanides : definition
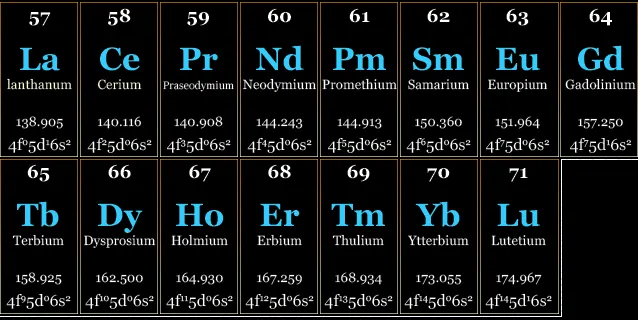
They are usually split into light rare earths (or cerics), which range from lanthanum to samarium (57 to 62) and heavy rare earths (63 to 71), ranging from europium to lutetium.
What are rare earth elements in geology ?
Rare Earth Elements (REE) : definition
Although scandium and yttrium are not part of the lanthanides, they have similar properties and are therefore also considered rare earths. The term "rare earths" is misleading. In reality, these elements are not necessarily rare in the Earth's crust; some, like cerium, are more abundant than lead. However, they are rarely found in exploitable concentrations and are often dispersed in various minerals, making their extraction difficult and expensive.
Rare earths have unique magnetic, catalytic, and phosphorescent properties that make them essential for many modern technologies. Here are some of their main applications :
- Electronics : Used in smartphone displays, televisions, computers, and lasers.
- Magnets : Neodymium (Nd) and samarium (Sm) are used to make very powerful permanent magnets, essential in wind turbines, electric motors, and hard drives.
- Batteries and Renewable Energy : Used in electric and hybrid vehicle batteries.
- Aerospace and Military : Present in high-performance alloys, guidance systems, and radars.
- Catalysts : Used in car catalytic converters to reduce exhaust emissions and in various industrial chemical reactions.
Rare earths are crucial to many high-tech industries, making them a strategic issue for countries that depend on them. China, which has about 37% of the world's rare earth reserves, is the main producer and exporter, giving it a dominant position in the global market. This dependence on China for supply has led several countries to seek to diversify their sources and develop recycling and substitution technologies for rare earths.
