MICA
Class : Silicates
Subclass : Phyllosilicates
Crystal system : Monoclinic
Chemistry : WX2-3 1-0Z4O10A2
Rarity : Very common
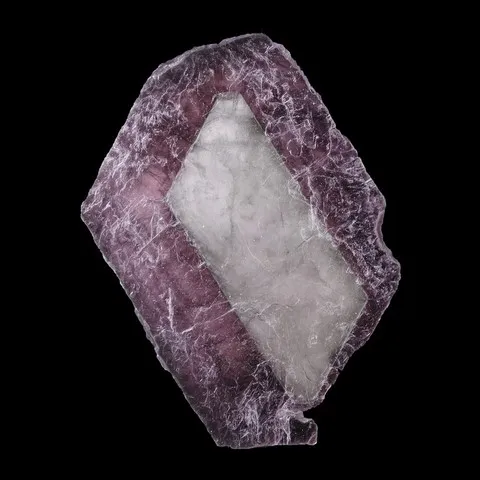
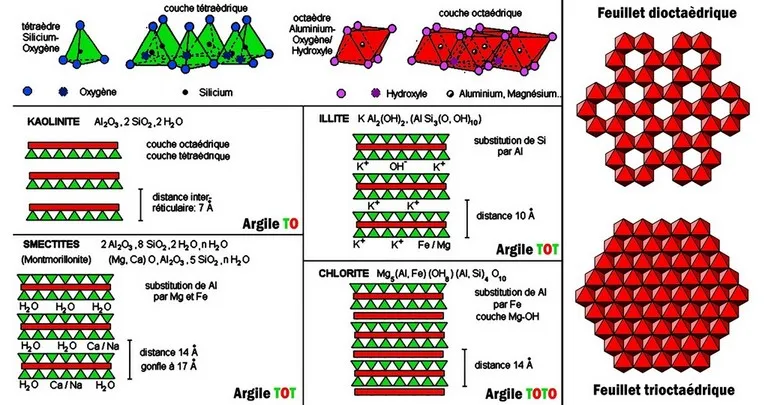
Mica is a generic term designating a group of sheet minerals, of monoclinic symmetry, and of general formula XY2-3Z4O10(OH,F)2 with X = Ba, Ca, Cs, K, Na ; Y = Al3+, Cr3+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Li+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Mn3+, V3+; Z = Al3+, Be2+, Fe3+, Si4+. This name comes from the Latin mica (crumb) or micare (to shine), recalling the ease with which the minerals of this group can fragment into shiny flakes. Micas are characterized by excellent basal cleavage which allows very easy lamellar flow, making them easily recognizable.
The structure of the micas is based on the alternation of sheets with 3 layers of the "TOT" type welded together by large cations (K, most often). The micas are divided according to the filling of the octahedral layer : they are said to be dioctahedral when 2 octahedra out of 3 are occupied by cations, and trioctahedral when the 3 octahedra are occupied.
The nature of the cation in the tetrahedral site depends on the nature of the mica : with Mg we obtain phlogopite, Mg and Fe biotite, Al muscovite, Li and Al lepidolite. In these micas, a quarter of the Si atoms are replaced by Al. Further substitution of Si by Al allows the integration of divalent cations: Ca2+ or Ba2+, resulting in "hard micas", margarite and clintonite. The physical properties evolve in parallel : loss of flexibility, ease of cleavage, etc...
The industrial uses of micas are relatively limited, and linked to their sheet structure which gives them insulating capacities and a good ability to structure synthetic materials.
Micas in France and in the World
Twinning
Refer to the individual sheets of each species to learn more about their twins and their special crystallizations.
Fakes and treatments
Hardness : 2 to 4
Density : 2,7 to 3
Fracture : Irregular
Trace : Variable
TP : Opaque to transparent
IR : Variable
Birefringence : Variable
Optical character : Variable
Pleochroism : Variable
Fluorescence : Variable
Solubility : Hydrofluoric acid
Magnetism : Variable
Radioactivity : Variable