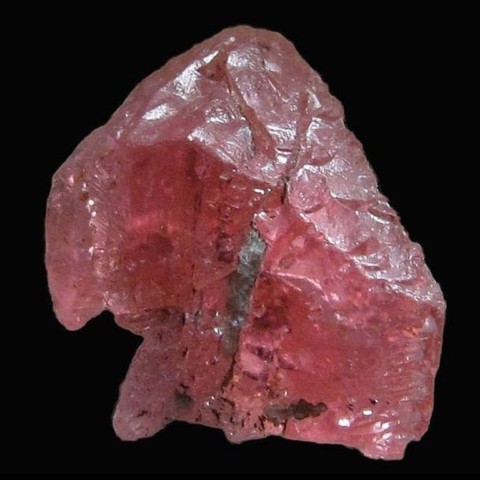
TRIPLITE
Class : Phosphates, arsenates, vanadates
Subclass : Anhydrous phosphates
Crystal system : Monoclinic
Chemistry : (Mn,Fe,Mg,Ca)2(PO4)(F,OH)
Rarity : Fairly common
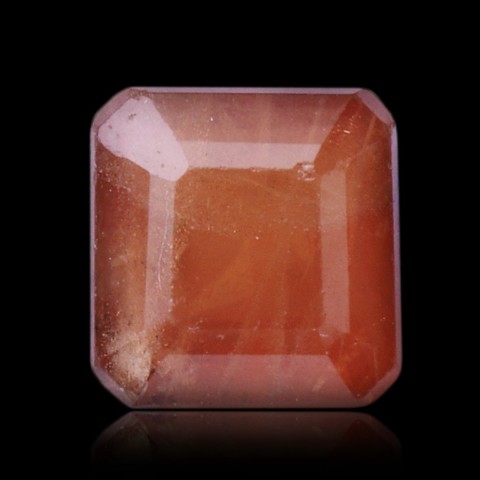
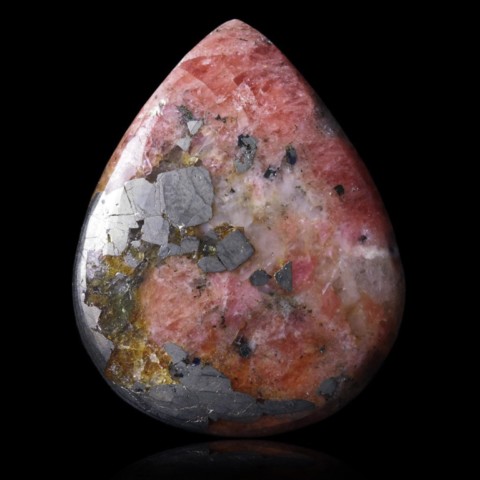
Triplite is a complex phosphate of manganese and iron that forms a continuous series with zwieselite, its iron equivalent. Low magnesium and calcium contents may appear. It is a mineral of granitic pegmatites, mainly sodolithic pegmatites where it accompanies lepidolite and triphylite. Its name comes from the Greek triplos (triple) in reference to its three cleavages. Triplite constitutes few crystals, it is usually massive, dark brown to brown, sometimes salmon to reddish when it contains little iron. Like many manganese carbonates and phosphates, it weathers black, releasing manganese oxides and generating a series of secondary hydrated manganese phosphates. It is occasionally cut into gemstones and cabochons.
Main photo : Triplite from Shigar Valley, Pakistan © Rob Lavinsky
Triplite in the World
Twinning
No twin known for this mineral species.
Fakes and treatments
No fakes listed for this mineral species.
Hardness : 5 to 5.5
Density : 3.5 to 3.9
Fracture : Irregular to conchoidal
Streak : White to brown
TP : Translucent to transparent
RI : 1.650 to 1.691
Birefringence : 0.030
Optical character : Biaxial -
Pleochroism : Visible
Fluorescence : None
Solubility : Acids
Magnetism : NoneRadioactivity : None