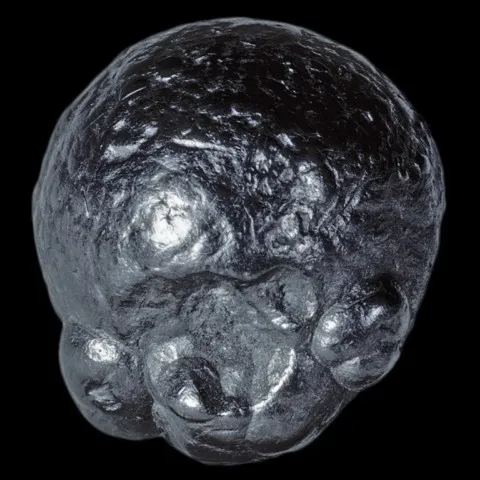
GRAPHITE
Class : Elements
Subclass : Non-metals
Crystal system : Hexagonal
Chemistry : C
Rarity : Common
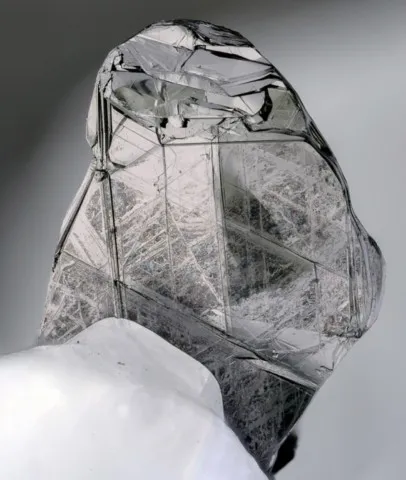
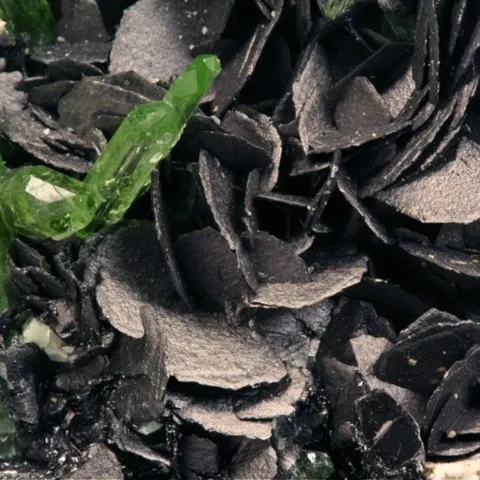
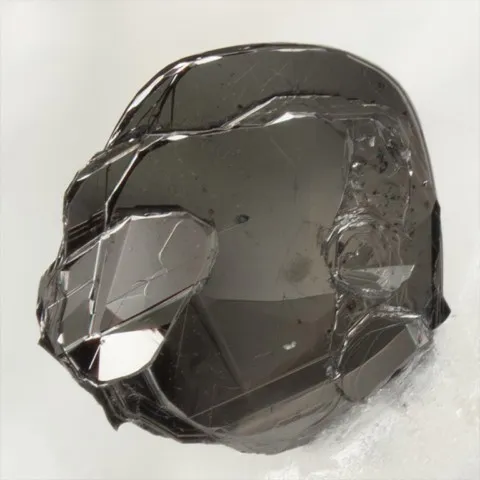
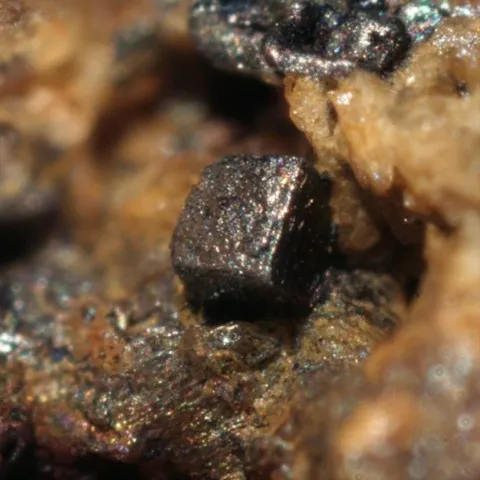
Graphite is, with diamond, lonsdaleite and chaoite, a polymorph of carbon. Graphite has a sheet structure. Each layer is made up of the juxtaposition of rings with six carbon atoms, and connected to the others by very weak Van der Walls forces, at the origin of the good cleavage according to {001} of this mineral. Graphite is usually present in metamorphic rocks coming from sediments rich in organic matter, sometimes in magmatic rocks having assimilated carbonaceous materials, rarely in granitic pegmatites. Its name comes from the Greek graphein (to write) due to its ancient use as a pencil. It is a black mineral with a metallic luster, staining the fingers because of its low hardness and its strong micaceous cleavage which causes it to disintegrate into fine flakes. Tabular hexagonal crystals, sometimes bordered by distinct isoscelohedra, are rare, usually centimetric, but can exceptionally reach 20 cm. Graphite most often occurs in stacks of shapeless micaceous lamellae, in irregular foliated masses, or in masses of amorphous appearance ; it is also earthy or in globular aggregates with a radiated structure. The industrial applications of graphite are numerous. If its use as pencil lead, inaugurated around 1550, is today anecdotal, its specific properties mean that it is found in numerous industrial sectors : lubricants (thanks to its low hardness of 1 to 2), refractories (chemical crucible, thanks to have a very high melting point: 4492°C), nuclear industry (neutron retarders). The production of synthetic graphite, however, clearly exceeds mining production.
Main photo : Graphite from Rhein Property, Amity, New York, USA © Pasquale Antonazzo
Graphite in the World
Fakes and treatments
No fakes recorded for this mineral species.
Hardness : 1 to 2
Density : 2.09 to 2.23
Fracture : Micaceous
Streak : Black to gray
TP : Opaque
RI : -
Birefringence : -
Optical character : Uniaxial -
Pleochroism : None
Fluorescence : None
Solubility : Insoluble
Magnetism : DiamagneticRadioactivity : None